In order to estimate how much in sales your startup can hope for, you’re going to have to estimate the market size for your product/service(s). This is critical for your startup because it will give you an idea of your business’ potential. It will also help you plan for capacity-related issues.
2 approaches to estimating the market size for a business plan
I cover this topic more in-depth in a post on market size and growth rate on my sister site, InvestSomeMoney.com.
The context there is focused on investing your money in a publicly-traded company. Though that’s a little different than what we are doing here, the fundamental principles remain the same.
The goal is to determine how many potential customers there are for a business and how much they are willing to spend. In order to do that, we can employ two general methods. These methods are a top-down analysis and a bottom-up approach to understand market size and growth.
One way to think about this is that a bottom-up approach uses multiplication and a top-down analysis uses division to arrive at an estimated market size.
After writing on this subject several times, I’ve come up with another way to think about these methods. I think a bottom-up approach should look internally, at things like unit size and capacity. A top-down analysis should look externally at things like demographics and market research.
Looking at this from these two different perspectives opens the door for further analysis. When you’re done, you should know whether you can expect to be capacity constrained or demand constrained. You’ll also start to flesh out some ideas that will help you further into your business plan.
If you do an analysis with both approaches, you can compare the results. For instance, if your bottom-up approach is higher, you’ll know that you could have excess capacity issues. You need to consider scaling that back or otherwise expanding your product/service offering to drum up additional demand.
Conversely, if your top-down analysis reveals that demand is in excess of capacity, then you are leaving money on the table. Time to start thinking about what you can do to scale up and capture as much of the market as possible.
Let’s start by taking a look at a bottom-up approach to estimating the market size for a business plan.
Bottom-up approach example
On my sister site, InvestSomeMoney.com, I researched three real-life examples of a bottom up market sizing approach. In those examples, you’ll see that they sometimes mix in a little top-down analysis with their bottom-up approach and vice versa. There’s no rule against doing that, but I would rather look at things from two totally different perspectives.
When using a bottom-up approach, try to start with the most simplistic piece of firm information you can get your hands on. Then, start to build on it with other information, or the best guess you can muster.
You can think of a bottom-up approach as one that focuses on how much and how often customers will buy.
This information might be something you have internally. Or, it might be from the information you found by researching online. Start with a single “serving size” of your product/service. Then, think about how often a customer would buy. Work your way up from there.
A bottom-up approach for my business plan
As mentioned in earlier posts about business plans – I’m building one as I write these. My theoretical product is an all-natural topical hair loss treatment.
In the post linked above, I performed something of a top-down analysis of market size for a business plan. I later discovered that I was operating with incomplete information.
There’s still a lot to consider regarding packaging volume and dosage. That will require more thought. But, for the time being, I’m going to estimate the volume of a one month’s supply and the daily dosage to be the same as Rogaine. If that changes as I progress with my business plan, I can easily circle back to this and plug in different numbers.
With Rogaine as my benchmark, I know that a dosage of my product would be 1 mL. The product would be used twice a day. My product would come in 2 oz (60 ml) bottles. Each bottle would be one month’s supply, as I said.
Thinking about capacity
Okay. Now that I have a grasp on the package size – what about blending and packaging? If this idea were to come to fruition, I don’t picture myself blending batches in my bathtub and filling bottles with a ladle and a funnel. I would need access to some sort of industrial equipment.
Fortunately, a quick internet search shows that there is no shortage of contract blenders and packagers out there. Especially for food and supplements. What it costs, remains to be seen. That’s an issue for another time. For now, I just want to get an idea of how much I could manufacture.
This company claims it can blend 1.25 million pounds per workday. We’ll assume, for now, this represents the average contract blender/packager. What does that translate into in terms of 2 oz bottles?
First of all, I wouldn’t need all 26 of their kettles. Only one, tops, especially at startup. So, if we divide the 1.25 million pounds by 26, we get a per kettle capacity of about 48,000 lbs per day.
Pounds are a weight unit of measure (UOM) and ounces are a volume UOM. To make the conversion, we’re going to have to do some more estimating.
Water weighs a little over 8 lbs/gallon. We’ll assume my product has roughly the same density.
8 lbs ÷ 128 oz (per gallon) = .0625 lbs/oz. With each bottle containing 2 oz, we know that it’ll weigh approximately .125 lbs/bottle.
This means that with one of this company’s kettles, I could blend 384,615 bottles worth of product per day. 96.5 million bottles per year. At an approximate sales price of $7.50 per bottle, that translates into nearly $725 million in revenue per year.
Okay, I’ve looked at things from a bottom-up, capacity-focused approach. Let’s now consider a top-down, demographic-focused analysis.
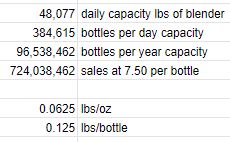
Top-down analysis
Not surprisingly, I also wrote a post on InvestSomeMoney.com with examples of a top-down analysis to determine market size for a business plan. When you read through it, you might notice that some of the examples use Census data (or something similar). They take big chunks of information and start narrowing down their market from there.
Which brings us to three important terms for performing a top-down analysis. These are:
Total addressable market (TAM)
Serviceable available market (SAM)
and
Serviceable obtainable market (SOM)
A SOM is a fraction of the SAM. In turn, a SAM is part of the TAM.
The TAM can be thought of as every potential customer that you can reach geographically. The SAM is what’s left when you niche down a little into the population that is a good fit for your unique selling proposition. Finally, the SOM represents the percentage of the SAM you can realistically expect to take.
It’s unlikely that you will ever capture 100% of the SAM. Even in a specific niche, you can’t be everything to everyone. That’s alright, though. The goal of this exercise is to make realistic estimates so that you have a sound business plan to work from.
When doing a top-down analysis, start with a large population or an overall industry size. From there, narrow down your customer until you arrive at your SOM. It helps to have a “customer avatar” in mind before starting a top-down analysis so you know where to niche down to.
I would suggest you perform a business plan demand analysis first to get a crystal clear picture of what that avatar is. You might think you know it intuitively. But you might be surprised at what you find – like I was!
A top-down analysis for my business plan
I know that not every person in the U.S. (much less the world) is going to want or need an all-natural topical supplement for hair loss. Who might though???
I’ll refer back to my handy-dandy business plan demand analysis (linked above) to see what I can find.
Here, I’m reminded of the ages that men and women first started experiencing hair loss. I’m reminded of the percentage that has sought any sort of treatment. Finally, I’m given an idea of what types of treatment they have tried.
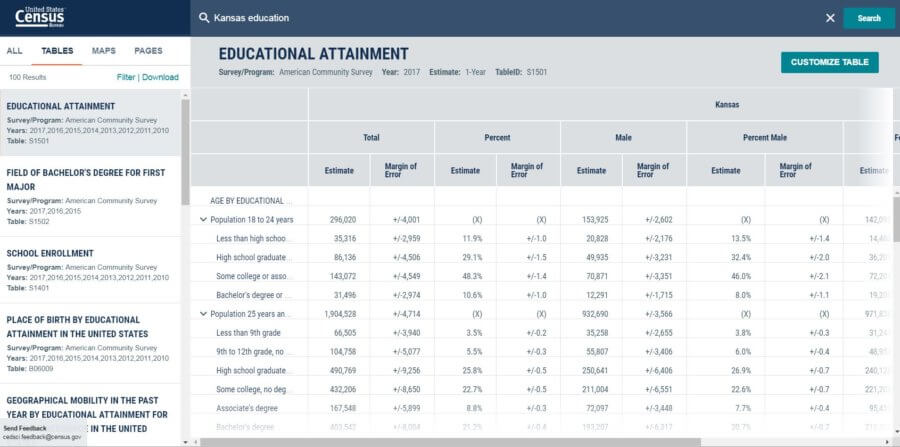
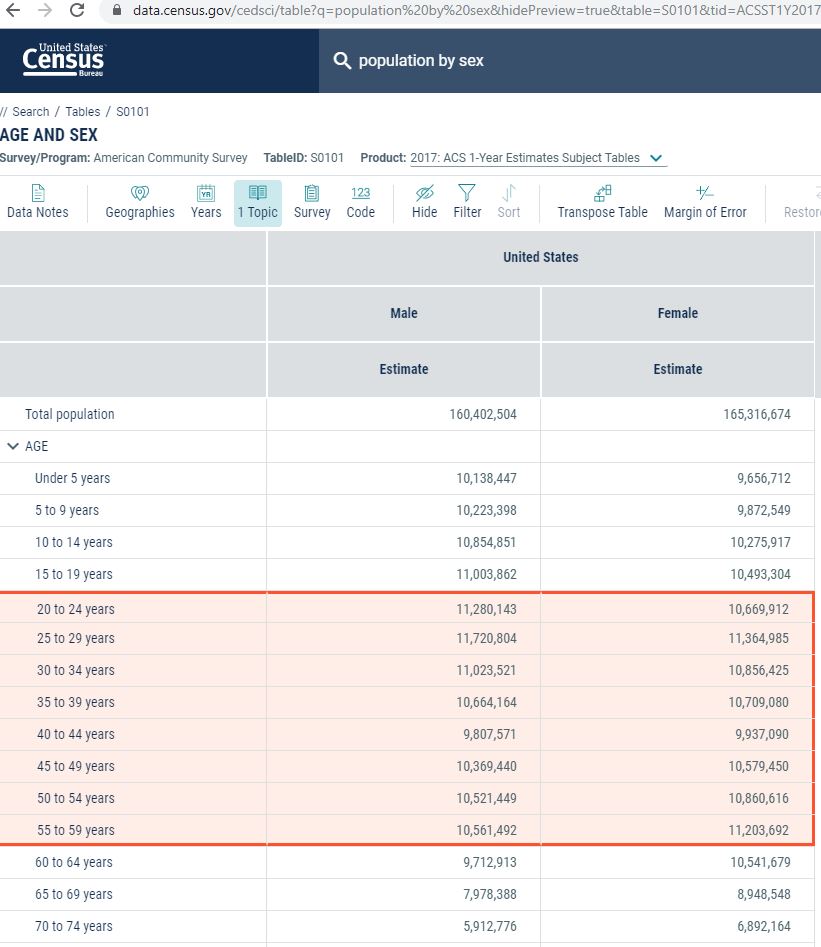
A quick visit to Data.Census.Gov and I find table S0101, which gives me the U.S. population by age and sex. I customize and filter the table real quick. Then, I copy and paste the data I need into my spreadsheet.
Next step is to narrow these numbers down. I’ll use the “regular” numbers and the pessimistic numbers from sensitivity analysis from my business plan demand workbook.
I want to know the percentage of men who have had hair loss and tried any sort of treatment. Then, I want to go deeper and estimate the number that has found supplements to be effective. I’ll do this for both the most-likely and the worst-case scenarios. On the women’s side, I’ll do, more or less, the same thing.
TAM and SAM
You’ll see that I didn’t use the same age ranges for men and women. I assumed that males would start experiencing hair loss earlier, but would also stop caring about it earlier too.
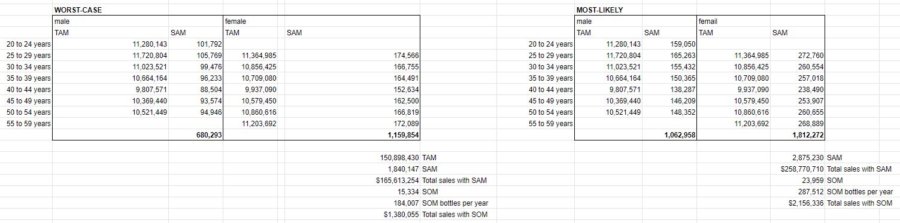
The age range for males in my TAM was 20 – 54. For females, it was 25 – 59. This translates into a TAM of 151 million people in the U.S.
For the SAM, my worst-case scenario estimated that .9% of the male population in the target age ranges would be part of my market. 1.54% of females in the target age ranges were also assumed to be part of my market. This translated into a worst-case SAM of 1.8 million people.
As for my most-likely SAM, I estimated that 1.41% of males and 2.4% of females in the target age ranges were potential customers. This resulted in a SAM of 2.88 million people. Over a million more potential customers.
SOM
SOM is tricky.
Who’s to say what percentage of the SAM my company could capture? Obviously, it would start at 0% and work its way up from there. Where would it stop though?
It will depend, in part, on the number of companies vying for this niche. As I often do, I will refer to the Pareto principle. The Pareto principle states that 20% of the inputs will be responsible for 80% of the outputs. Put another way, 20% of the companies will have roughly 80% of the market share.
I’ll refer back, again, to my post on business plan demand. In it, I found three direct substitutions for my topical hair loss product. I won’t include Minoxidil (Rogaine) in that group, because of its unnatural chemistry.
Again, without getting too mired in math, I estimate that there are approximately thirty companies in the topical hair loss supplement space. This was a quick and dirty estimate based on the results of an internet search.
Six of those thirty companies probably control 80% of the market. That leaves 4.2% (1 ÷ 24) of the remaining 20% as my short-term SOM. Obviously, if my product were to take off, that amount could grow considerably and could approach the SAM.
What that means as far as the market size is 15K people worst-case and 24K people most-likely. At 12 bottles purchased per year, this translates into 184K and 287.5K bottles per year respectively.
Here’s a look at the spreadsheet breaking that all down:
Comparing a bottom-up and top-down analysis when determining market size for a business plan
Obviously, a couple hundred thousand bottles (top-down) is a far cry from 96.5 million (bottom-up). So, it would appear I will not be capacity constrained in the near future. In fact, as this startup moves forward, I need to make sure I’m not over-buying capacity. Those huge fixed costs could kill my business before it has a chance to get off the ground.
Speaking of fixed costs, the information from this analysis has given me good data to build my pro forma financials – when that time comes.
Now, at some point in the future, selling my product internationally could be an option. However, in this tiny niche, it is unlikely that I’ll ever need that much capacity for this one product.
Market size for a business plan
What were there factors I didn’t consider (but should have) when estimating my potential market size?
How might you have approached this differently?