Customer profitability is measured by subtracting allocated costs from customer revenue.
The trick is to logically allocate costs – specifically Selling, General, and Administrative expenses. Understanding your customer profitability will help you make better decisions. For instance, what new customers to target and which of your current customers to part ways with. Having more good (and less not-so-good) customers will make your life as a small business owner more enjoyable.
Download a copy of the Customer Profitability workbook
Complete the form below and click Submit.
Upon email confirmation, the workbook will open in a new tab.
Why is it important to analyze customer profitability?
You’re probably wondering if some of your small business’ customers are unprofitable.
In the back of your mind, you know that some customers are better than others. Some customers are a huge headache and don’t bring in that much revenue. Others are a pleasure to do business with and drive the majority of your revenue.
It’s more than just revenue
Sure, you have an inkling of which customers are good and which are… not-so-good. But until you run the numbers, you’ll never know.
What you find might surprise you. Maybe the customer who’s a huge headache is worth it? Or, maybe the customer who seems ideal is actually unprofitable?
Revenue is the starting point. But customer profitability has as much to do with costs as it does revenue.
Build a better business with a customer profitability analysis
By understanding which of your customers are the most profitable, you can make better decisions in the future.
You will have a measurement to decide if you need to dedicate more time and resources to certain customers. Or, if you need to fire them.
Your “ideal customer” will become clearer. This will allow you to focus your marketing toward other “ideal customers.”
Also, by getting rid of not-so-good customers, you’ll likely save a huge emotional toll on yourself and your employees. Work will become more pleasurable. Which, in turn, can only help you achieve your vision for your small business.
How does a business measure customer profitability?
You know that profit = revenue – expenses. So, customer profit must equal customer revenue – customer expenses.
Customer revenue is easy enough. Your accounting software should be able to provide you with a report that tells you what you sold to who. If not, that’s Job #1 – to piece together this information or start measuring it going forward. You can’t measure customer profitability without it.
If you’re following along in the Customer Profitability workbook, you can enter customer names in row 5 of the Customer Profitability worksheet. Additionally, enter Customer revenue in row 7.
Also, for the sake of consistency, I would advise you to enter a Start and Finish Time period. This goes in cells C3 & D3 respectively. These dates won’t affect any formulas. They will, however, help ensure that your revenue and costs are compared consistently.
Costs of Goods Sold/Cost of Sales
Cost of goods sold (COGS), also known as Cost of sales (COS), are the costs your business (more or less) directly incurred to deliver that product/service to the customer.
Again, your accounting software probably captures this for you in a report somewhere.
QuickBooks Online captures this information in a report called Profit and Loss by Customer. It can be found by navigating to Reports (left menu) > Standard (tab) > Business overview (section).
Here’s what that report looks like when downloaded into a spreadsheet:
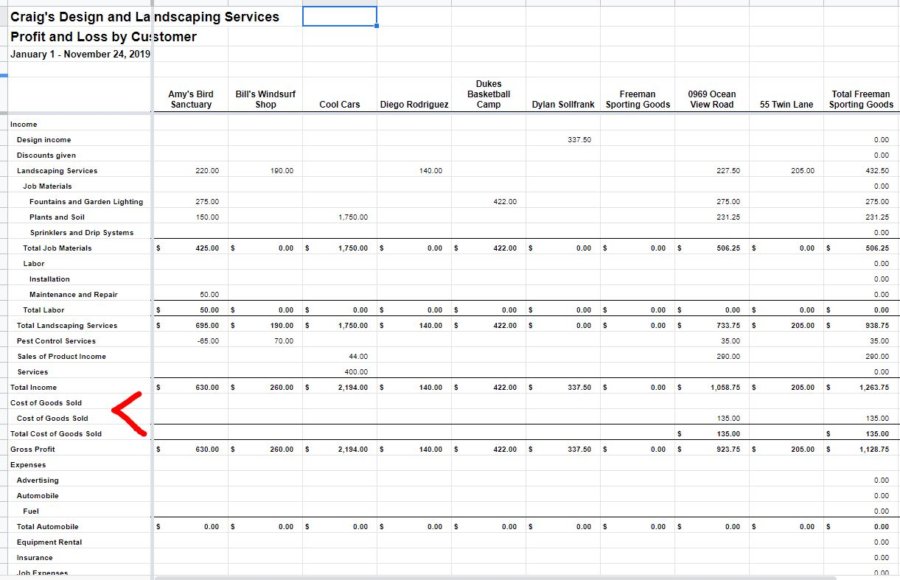
Click to enlarge
Based on how you set up your customers and products/services in QBO, your COGS will automatically be recorded in this report. That’s a big chunk of costs right there! Customer Gross Profit is taken care of.
Learn more about gross profit maximization here.
What if you don’t have a report that totals customer revenue and COGS?
You can estimate these totals with the Customer Rev/COGS (Optional) worksheet. It will just take a little more legwork.
First, list all your Products/Services in column B. Then for each Product/Service list the average Price you sell it for. Also, the average Cost.
Again, I’ll try not to get too technical. “Cost” in this case, includes material, labor, and overhead. The total costs incurred to produce one Product/Service. If you’re unsure whether to include a particular expense, leave it off. It can always be allocated on the Customer SGA Allocation worksheet.
After you’ve listed Products/Services, Price, and Cost, then you’ll want to enter the QUANTITY PURCHASED by each customer.
At the bottom, you’ll see Revenue and COGS by customer summed. These amounts can then be entered on the Customer Profitability Worksheet. They won’t carry over automatically because this worksheet is optional.
With Customer revenue and Customer cost of goods sold entered, Customer gross profit and gross margin will be calculated. Your Customer Profitability worksheet should look something like this:
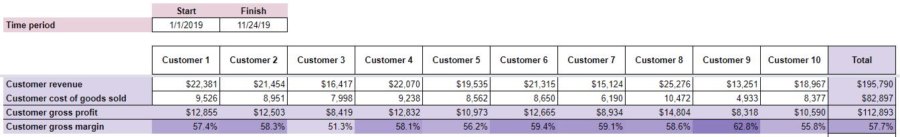
The shading of the Customer gross margin cells will change slightly to highlight those customers with the highest gross margins.
What about Selling, General, and Administrative expenses?
Everything up until this point has been fairly intuitive. This is where the good customers get separated from the not-so-good, though.
Selling, General, and Administrative (SGA) are those expenses that are not directly tied to any individual Product/Service. This is why you don’t see these expenses included in the QBO Profit and Loss by Customer report.
But, these expenses are very real. They are (or, at least, should be) necessary to serve your customers. So, they should be accounted for any time you speak of “profitability.”
How do you allocate these expenses to individual customers though?
You can think of each type of Expense as a pie. It’s up to you to decide on the most appropriate way to slice that pie for each customer. There are no wrong ways to slice that pie. Some are just better than others.
Start by listing Expenses in column B on the Customer SGA Allocation worksheet. Break them down into as much detail as you’re comfortable with.
For each Expense, enter an Amount to be Allocated in column C. Remember to stick to the Time period specified on the Customer Profitability Worksheet. You don’t want to allocate too much or too little.
Drivers – slicing the pie
Now, comes the creative part…
Think about what drives that Expense. Specifically, what the customer does that makes that Expense increase.
For example, Automobile expenses could be allocated by the number of miles driven for a client. Meals and Entertainment could be allocated by the number of meetings and events you took part in with the client.
Again, there are no wrong answers here because there are (usually) no perfect ways to slice the pie. Use your best judgment. If you completely draw a blank, you can always allocate that Expense evenly across all customers.
Try not to do that if at all possible, though. It’s the allocation of these costs that really separates the profitable customers from the unprofitable ones.
Back to the Customer SGA Allocation worksheet.
Enter the method of allocation in column D. Then, for each customer, break the Amount to be Allocated down in that manner. The Total of that breakdown (column O) needs to equal the Amount to be Allocated.
If all of the Totals don’t match, you’ll see an error message in cell P25.
Customer SGA expenses are totaled at the bottom and carried over to the Customer Profitability Worksheet.
Your completed Customer SGA Allocation worksheet should look something like this when you’re done:
The final product
If you look back at the Customer Profitability Worksheet, you’ll see that Customer SGA expenses are subtracted from Customer gross profit to give you Customer operating profit. Aside from taxes, this is essentially your bottom line for customer profitability.
Customer operating margin is also displayed. Again, the shading in these cells will change to highlight those customers with the highest operating margin.
A chart, comparing your customers is also included to help with understanding.
Your final product should look something like this:
How to improve
Good news! The first step to improving customer profitability is to understand it. After using this workbook, you should have a better understanding of customer profitability.
Next, look for common themes among your best (most profitable) customers. Is there anything they have in common?
How did you acquire these customers? Can you replicate it?
Can you do more business with these customers? You don’t want to grind on your best customers too hard. But, are there any more of their problems you can fix with your solutions?
Don’t just look at your customers either. Look into the mirror a little bit too. Is your company making some customers not-so-good? This might not be comfortable. But, some introspection could help you convert some of those not-so-good customers to the light side.
If some of the not-so-good customers are hopeless though, you might have to fire them. This can be a delicate situation. However, sinking money into customers that you don’t even enjoy dealing with is destructive. Do your homework on the best way to do so and let them be someone else’s problem.




